Các Annotition trong Java
Các Annotition trong Java
@ConstructorProperties:
Được dùng để chỉ định tên của các tham số trong constructor tương ứng với các trường dữ liệu trong một lớp. Điều này thường được sử dụng khi bạn muốn ánh xạ các giá trị được truyền vào constructor với các trường cụ thể trong class.
Trong trường hợp này, danh sách các chuỗi được đưa ra trong ngoặc kép {…} đại diện cho tên của các trường mà constructor sẽ sử dụng để khởi tạo đối tượng. Ví dụ, khi bạn tạo một đối tượng từ lớp có constructor được chú thích với @ConstructorProperties, bạn cần truyền các giá trị tương ứng với các trường “status”, “userType”, và “moduleCode” vào constructor theo thứ tự này.
- VD:
import java.beans.ConstructorProperties;
public class MyClass {
private int status;
private String userType;
private String moduleCode;
@ConstructorProperties({"status", "userType", "moduleCode"})
public MyClass(int status, String userType, String moduleCode) {
this.status = status;
this.userType = userType;
this.moduleCode = moduleCode;
}
// Các getter và setter khác...
}
Khi bạn tạo một đối tượng MyClass, bạn cần truyền các giá trị cho status, userType, và moduleCode theo thứ tự được chỉ định trong chú thích @ConstructorProperties. Ví dụ:
- MyClass obj = new MyClass(1, “Admin”, “ABC123”);
Lưu ý rằng thứ tự của các tham số trong constructor phải khớp với thứ tự được chỉ định trong chú thích @ConstructorPropertie
@MappedSuperclass
-
Được sử dụng để chỉ định rằng một class là một superclass mà các entity khác có thể kế thừa các trường và phương thức từ đó.
-
Annotation này không tạo ra một bảng trong cơ sở dữ liệu cho class đó, nhưng các trường và phương thức của nó có thể được kế thừa bởi các entity khác được ánh xạ vào các bảng riêng biệt.
-
Điều này thường được sử dụng khi có một số lớp entity chia sẻ các thuộc tính chung mà không cần tạo ra một bảng riêng biệt cho superclass.
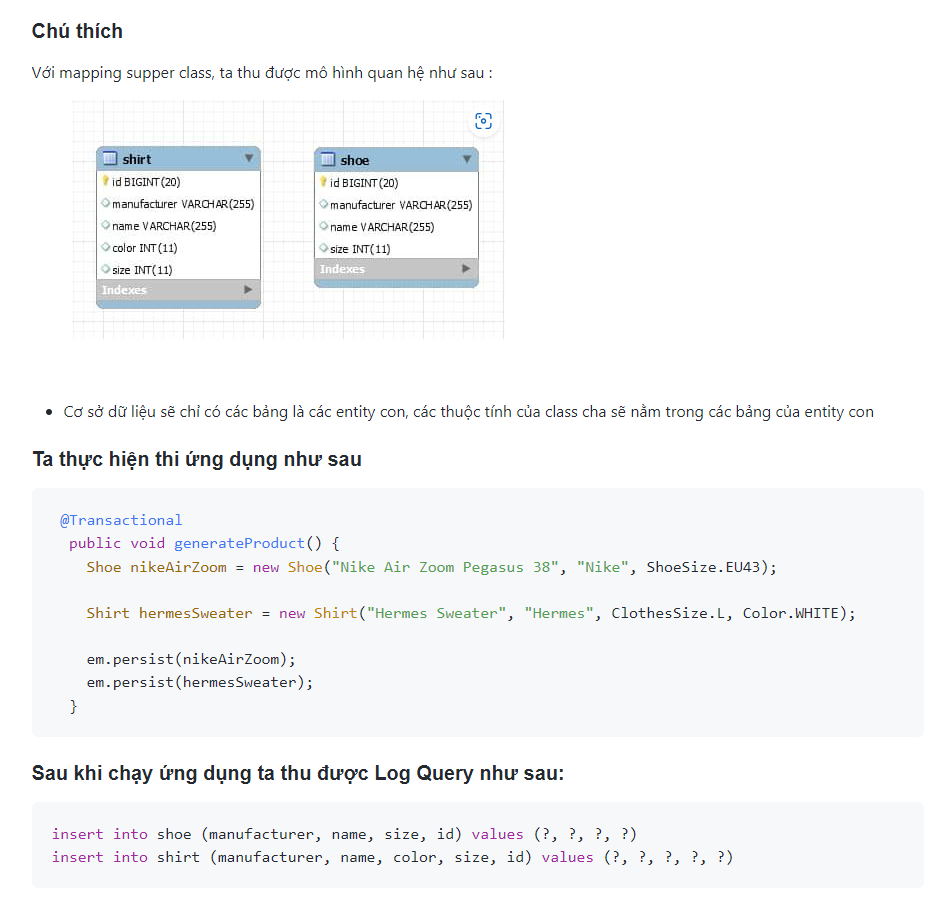
Ta có 1 class cha và 2 entity con như sau:
-
Class BaseProduct: class cha, không phải entity.
-
Shirt, Shoe: 2 entity con.
BaseProduct
@MappedSuperclass
public class BaseProduct {
@Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private long id;
//...
}
- Với cách này ta sử dụng annotation @MappedSuperclass ở class cha
Shirt
@Entity(name = "shirt")
@Table(name = "shirt")
public class Shirt extends BaseProduct{
//...
}
Shoe
@Entity(name = "shoe")
@Table(name = "shoe")
public class Shoe extends BaseProduct{
//...
}
Chú thích
@Inheritance
-
@Inheritance là annotation để chỉ định chiến lược kế thừa cho các entity.
-
@Inheritance(strategy = InheritanceType.JOINED)
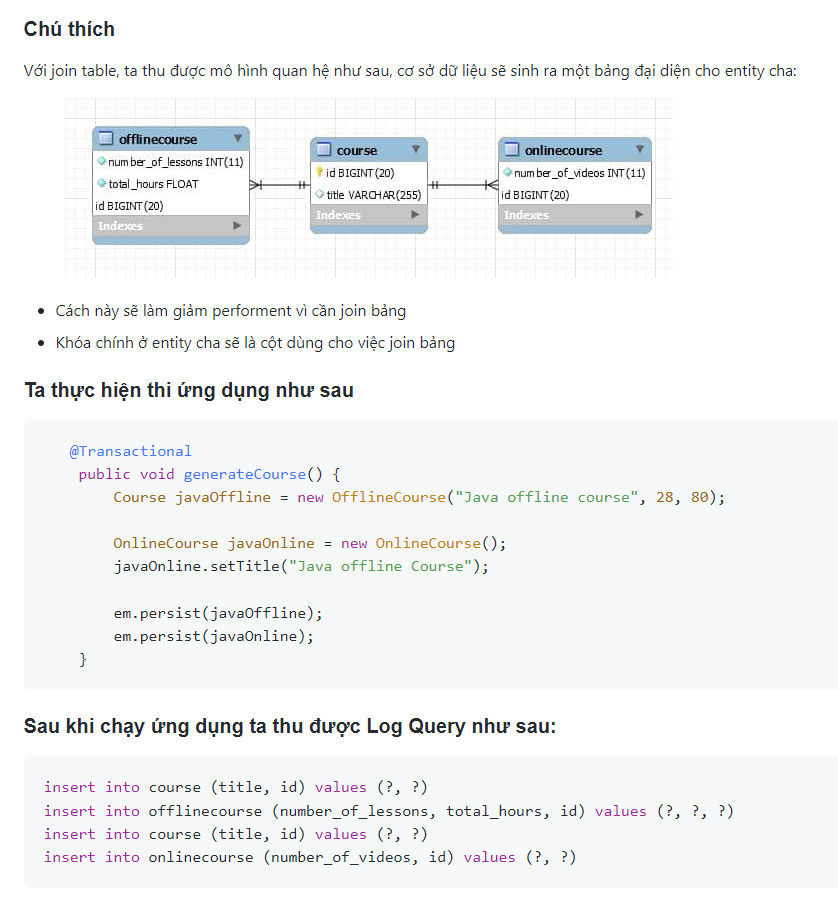
JoinTable:
Ta có 1 entity cha và 2 entity con như sau:
-
Abstract Course Entity: entity cha
-
OnlineCourse, OfffineCourse : 2 entity con
Course Entity
@Entity
@Inheritance(strategy = InheritanceType.JOINED)
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
public abstract class Course {
@Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
protected Long id;
//...
}
- Ta sử dụng annotation @Inheritance(strategy = InheritanceType.JOINED) ở entity cha
OnlineCourse Entity
@Entity(name = "onlinecourse")
@Data
public class OnlineCourse extends Course {
private int numberOfVideos;
}
Chú thích
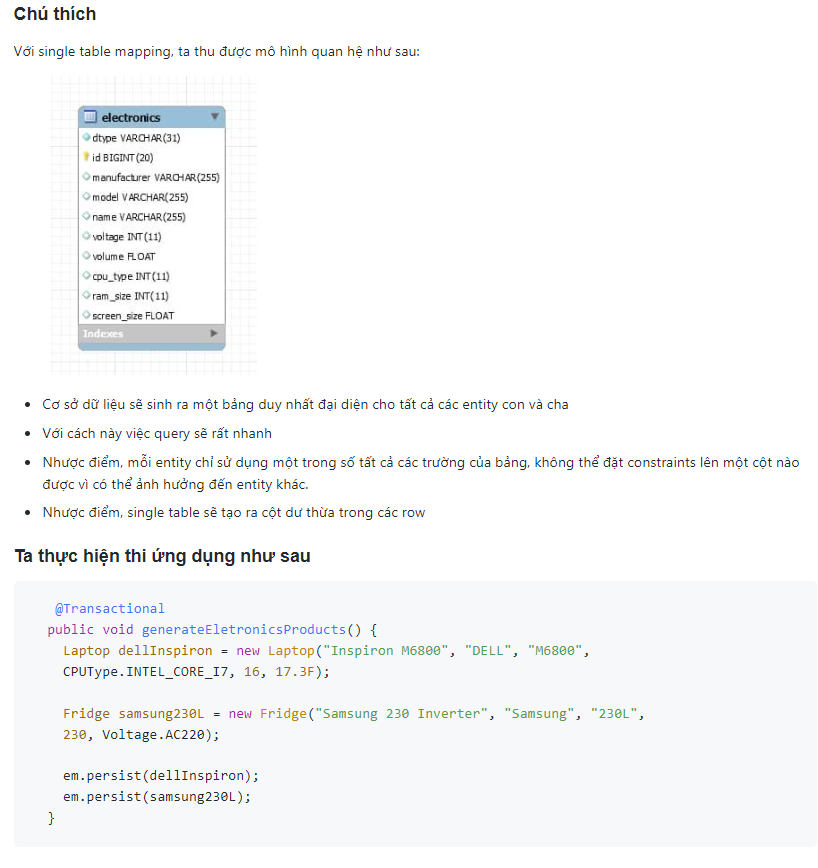
Single Table
Ta có entity cha và 2 entity con như sau:
-
Entity Electronics: entity cha
-
Fridge, Laptop: 2 entity con
Electronics
@Inheritance(strategy = InheritanceType.SINGLE_TABLE)
public class Electronics {
@Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private Long id;
private String name;
private String manufacturer;
private String model;
//...
}
- Ta sử dụng annotation @Inheritance(strategy = InheritanceType.SINGLE_TABLE) ở entity cha
Fridge
@Entity(name="fridge")
public class Fridge extends Electronics {
//...
}
Laptop
@Entity(name="laptop")
public class Laptop extends Electronics {
//...
}
Chú thích
Sau khi chạy ứng dụng ta thu được Log Query như sau:
insert into electronics (manufacturer, model, name, cpu_type, ram_size, screen_size, dtype, id) values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, 'Laptop', ?)
insert into electronics (manufacturer, model, name, voltage, volume, dtype, id) values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, 'Fridge', ?)
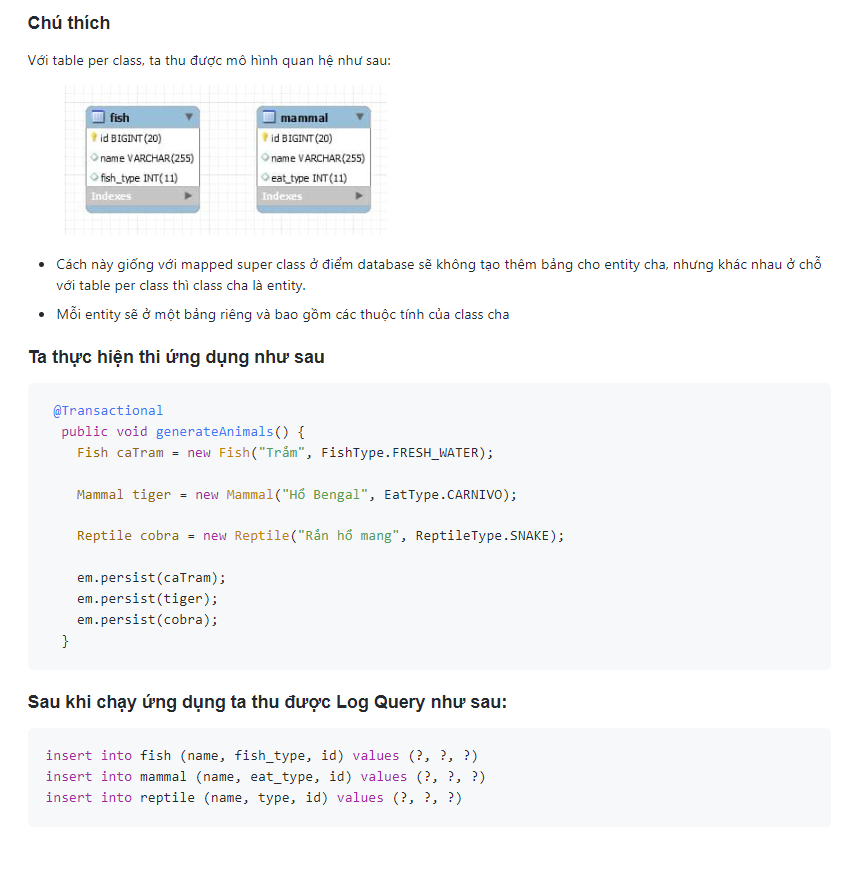
Table Per Class
Ta có 1 entity cha và 3 enity con như sau:
-
Animal: entity cha
-
Fish, Mammal, Reptile: 3 entity con
Animal
@Entity(name = "animal")
@Inheritance(strategy = InheritanceType.TABLE_PER_CLASS)
public abstract class Animal {
@Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private Long id;
private String name;
//...
}
- Ta sử dụng annotation @Inheritance(strategy = InheritanceType.TABLE_PER_CLASS) ở entity cha
Fish
@Entity(name = "Fish")
public class Fish extends Animal{
//...
}
Mammal
@Entity(name = "Mammal")
public class Mammal extends Animal {
//...
}
Reptile
@Entity(name = "reptile")
public class Reptile extends Animal {
//...
}
Chú thích